Spatiotemporal Transcriptomic Profiling Reveals the Dynamic Immunological Landscape of Alveolar Echinococcosis (Adv. Sci. 18/2025)
IF 14.3
1区 材料科学
Q1 CHEMISTRY, MULTIDISCIPLINARY
引用次数: 0
Abstract
Echinococcus Multilocularis
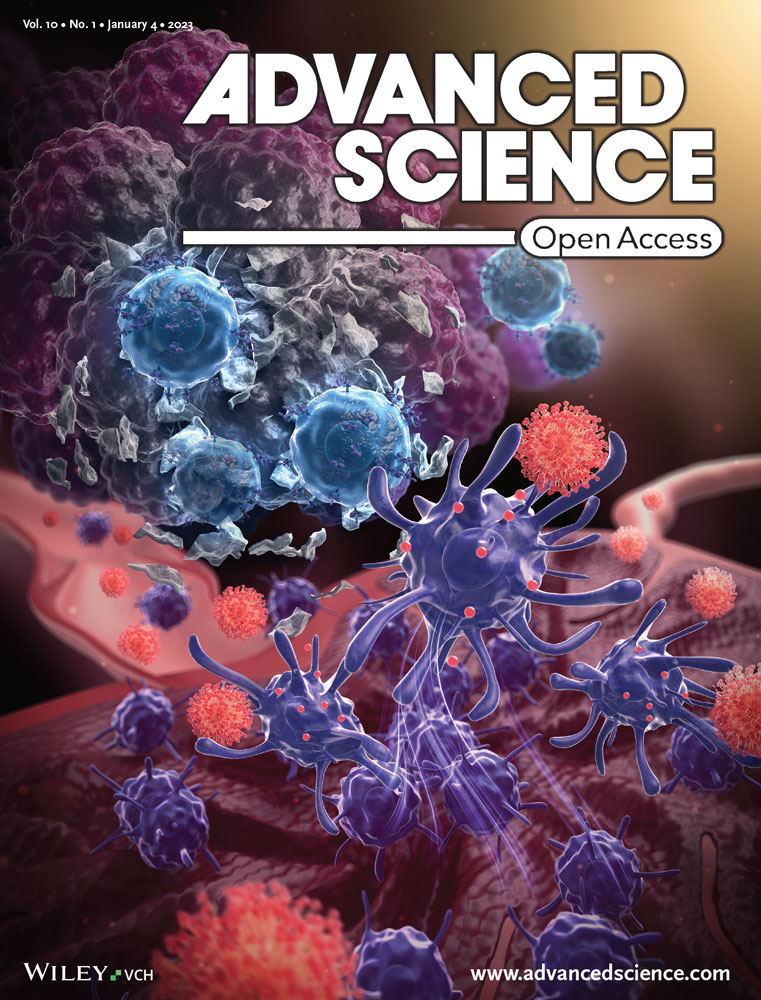
In article number 2405914, Wan-Zhong Jia, Junhua Li, Hong-Bin Yan, and co-workers decipher the shift in host (Nezha) immune response strategies from “active killing” to “negative segregation” during Echinococcus multilocularis hepatic infection. During the early infection stage, neutrophils (fire-tipped spear) and macrophages (wind fire wheels) collaborate to eliminate protoscoleces (goblins). In the middle and late stages, macrophages and fibroblasts (red armillary sash) cooperate to physically isolate the continuously expanding microcyst (monster).
时空转录组学分析揭示肺泡包虫病的动态免疫景观(Adv. Sci. 18/2025)
在文章编号2405914中,贾万忠,李俊华,闫洪斌等人破译了多房棘球绦虫肝脏感染期间宿主(Nezha)免疫反应策略从“主动杀伤”到“负分离”的转变。在早期感染阶段,中性粒细胞(火头矛)和巨噬细胞(风火轮)协同消灭原头节(小妖精)。在中晚期,巨噬细胞和成纤维细胞(红色腋窝带)合作,物理隔离不断扩大的微囊(怪物)。
本文章由计算机程序翻译,如有差异,请以英文原文为准。
求助全文
约1分钟内获得全文
求助全文
来源期刊
Advanced Science
CHEMISTRY, MULTIDISCIPLINARYNANOSCIENCE &-NANOSCIENCE & NANOTECHNOLOGY
CiteScore
18.90
自引率
2.60%
发文量
1602
审稿时长
1.9 months
期刊介绍:
Advanced Science is a prestigious open access journal that focuses on interdisciplinary research in materials science, physics, chemistry, medical and life sciences, and engineering. The journal aims to promote cutting-edge research by employing a rigorous and impartial review process. It is committed to presenting research articles with the highest quality production standards, ensuring maximum accessibility of top scientific findings. With its vibrant and innovative publication platform, Advanced Science seeks to revolutionize the dissemination and organization of scientific knowledge.
 求助内容:
求助内容: 应助结果提醒方式:
应助结果提醒方式:


